Está a punto de abandonar este sitio.
Por favor, tenga en cuenta que su carro de la compra actual no ha sido guardado todavía y no podrá ser restablecido en el nuevo sitio ni cuando regrese. Si desea guardar su carro de la compra, inicie sesión en su cuenta.

1D-Gradient? 2D-Gradient??
Academia de laboratorio
- Salud y medicina
- Amplificación y PCR
- Cicladores para PCR
- Ensayo
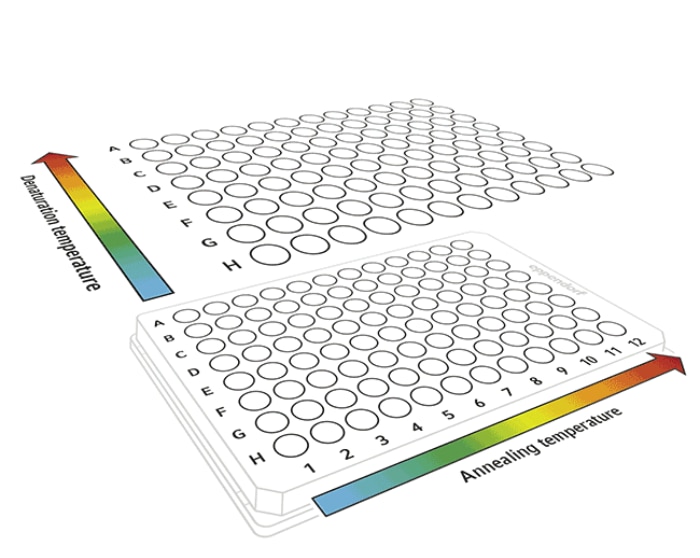
Indeed, 1D and 2D in gradient refers to 1-dimensional and 2-dimensional, respectively. Optimization of a new PCR protocol can be highly tedious, time-consuming and costly work. To address this, many conventional cyclers in the market now comes with gradient function. The gradient PCR you are familiar with is most probably the 1D generation technology. This one-dimensional gradient technology was pioneered by Eppendorf decades ago and was one of the most revolutionary function that drove the PCR field.
You’ve heard of 4D cinema, 4D digital printing, etc.… Now, gradients too come in dimensions?!
Now, we see another revolution in the gradient technology – the 2-dimensional or 2D-gradient. This technology enables the user to use two gradient steps in the same PCR. The original 1D-gradient gives 12 different temperatures horizontally across the block (some brand uses 8 temperatures across the rows from top to bottom strategy). With the new 2D-gradient, the thermal block can now additionally give 8 different temperatures vertically across the block. Both 2 gradients can be combined in one PCR program, thus allowing concurrent optimization of the denaturation step and the annealing step.
Leer más
Leer menos
Leer más
Leer menos
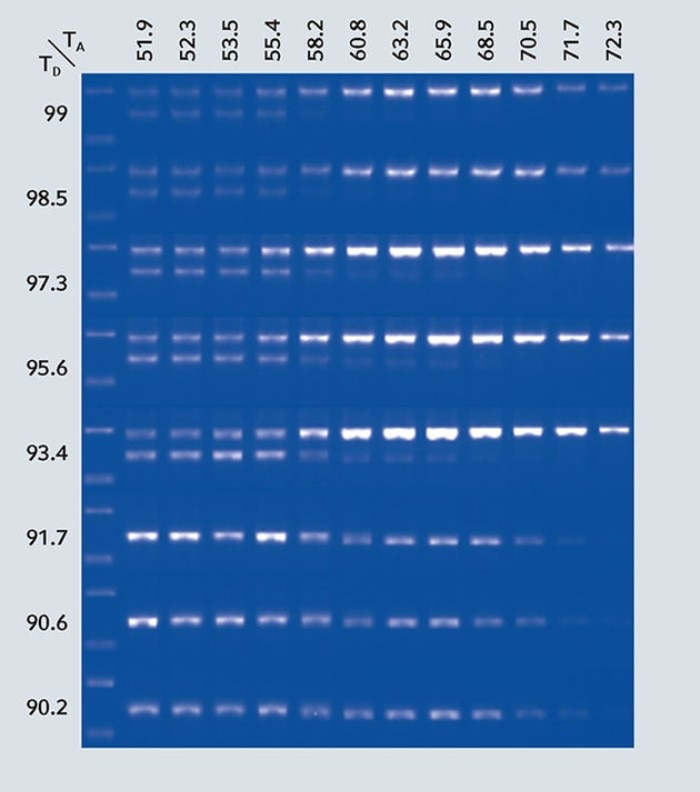
- Amplifying low concentration DNA target (use 2D-gradient to identify parameters to increase yield)
- Optimizing amplification of GC-rich DNA targets
- Optimizing 3-step PCR to 2-step PCR or even 1-step PCR (combining both denaturation and annealing or annealing and extension temperatures) to reduce time
- As troubleshooting tool for reducing multiple non-specific amplification bands (to use 2D-gradient to identify parameters that increase specificity)
- Multiplex PCR: amplification of multiple targets, which involves different regions of DNA (varying amplicon length and GC-content), thus making optimization of denaturation temperature beneficial. Examples of multiplex applications:
- Typing and analysis of transgenic organisms
- Amplification and analysis of microsatellites
- Typing and detection of bacteria and viruses
- Amplification of multiple DNA regions for SNP analysis
- Amplifying large plasmid (e.g those with long PCR amplicon). In such cases, the denaturation temperature might need to be increased for successful PCR and 2D-gradient can be used to simultaneously find out the best denaturation and annealing temperature at one go.
Leer más
Leer menos

